MISSION ® Predesigned siRNA were created using the proprietary Rosetta Inpharmatics siRNA Design algorithm in an exclusive partnership with Merck & Co The Rosetta siRNA Design Algorithm utilizes PositionSpecific Scoring Matrices and knowledge of the seed region to predict the most specific and effective sequences for your target genes The algorithm's rules were developedAlso, selection of an siRNA having a minimum of 2 mismatches with any other off‐target sequence can further reduce the probability of siRNA to bind to the undesired off‐target sequence 13 , 14 Along with seed region the effectiveness of non‐seed region of guide strand has also been reported in mediating off target effect but a negative correlation of T m value and GC contentKeywords RNAi, Offtarget effects, Data analysis, Seed region, miRNA, siRNA, shRNA, Highthroughput screening Background RNA interference (RNAi) is a posttranscriptional gene regulatory mechanism 1 that has been widely used for functional genomics studies both in cell lines and organisms The synthetic duplexes referred to as small inter fering RNAs (siRNAs) or short
Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife
Seed region sirna
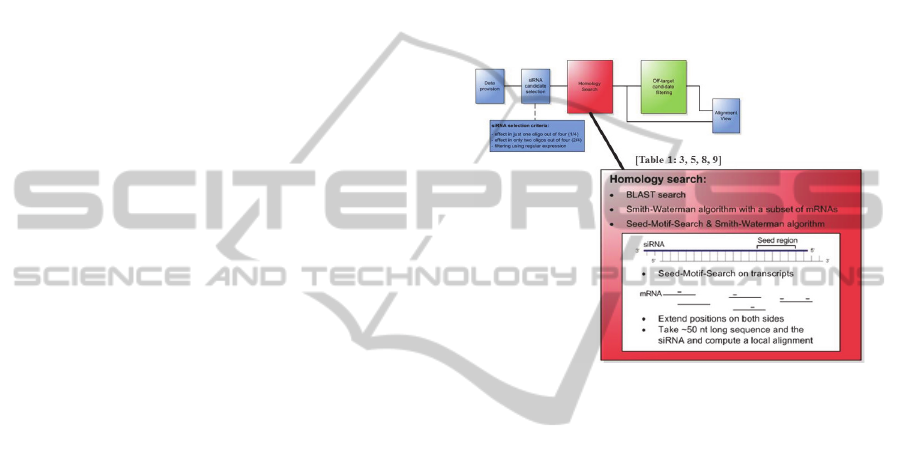
Seed region sirna-3' UTR/seed region analysis Intelligently weighted, multiparameter searches for matches of the seed region of the siRNA antisense strand with the 3' untranslated region of unintended mRNA targets are performed Minimizes risk of offtarget effects caused by siRNA acting like an miRNA 7–12 SNP avoidance The RefSNP database is used to exclude siRNAs which span single As the offtarget effects were identified based on perfect complementarity to the seed region (positions 2–8) and both terminal nucleotides of siRNA are known to be incorporated into Ago protein (positions 1 and 21), the potential basepairing between siRNA and offtarget mRNA was determined via positions 9– (ie 3' region) The number of GC and AU basepairs was




Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife
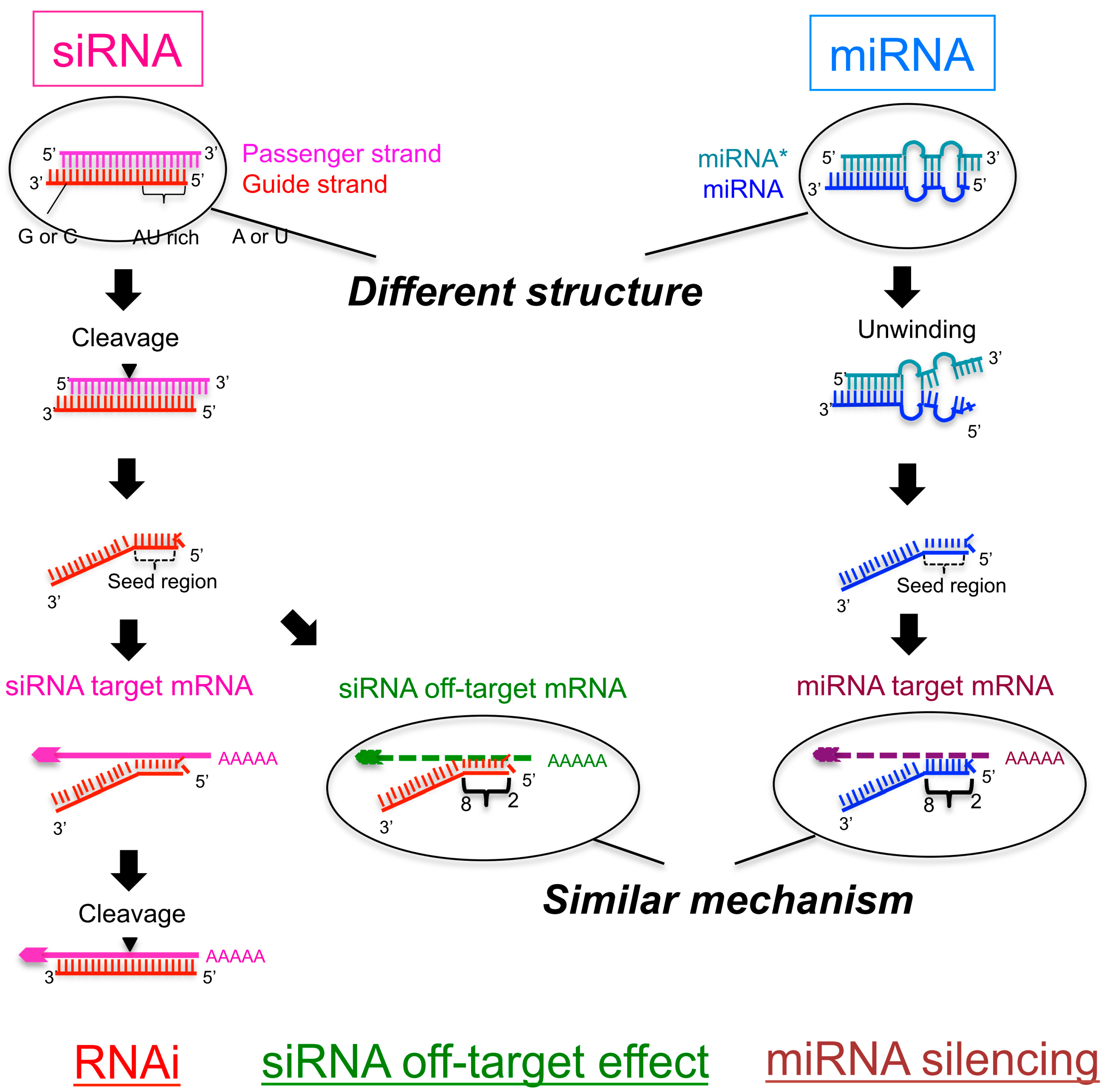
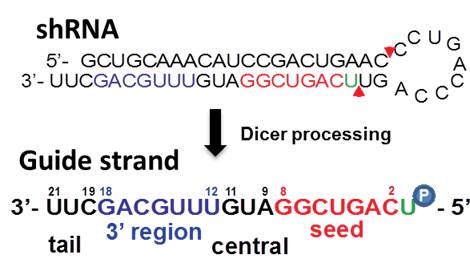
The seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementarySilencing is induced by the basepairing between the seed region at positions 28 from the 5' end of the RISCloaded siRNA strand, and its complementary sequences in the 3' UTR of the unrelated mRNAs 13 Although RNAi is now widely and routinely used as an experimental tool, the remaining fundamental concern is whether the target gene can be specifically silenced Several recent studies suggest that the main source of siRNAmediated offtarget gene silencing could be the complementation between the 'seed' region of
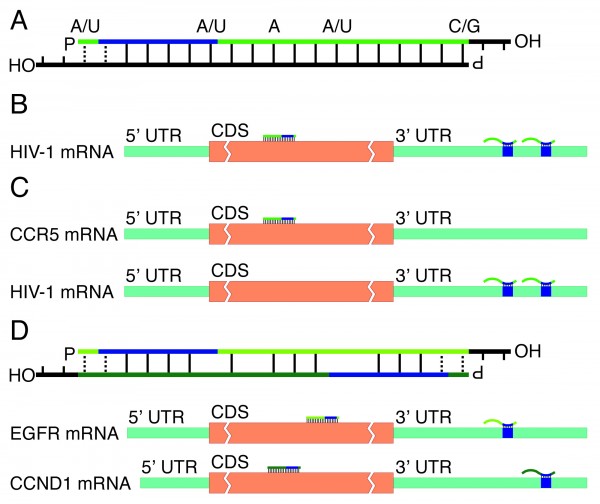
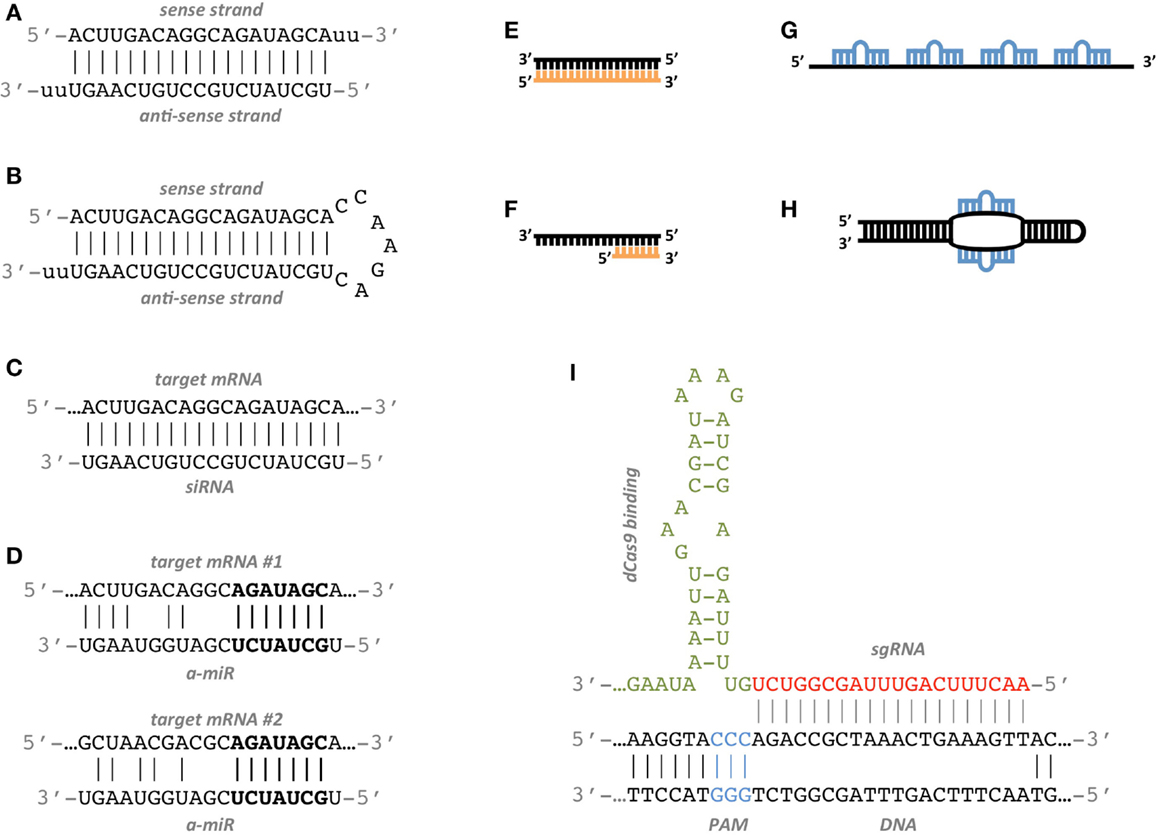
SiRNA is designed to be perfectly complementary to the target mRNA and, miRNA follows the "seed pairing rule", a complementary binding of miRNA seed region to binding site (BS) located in the mRNA 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) (Figure 1C) The seed region involves nt 28 from miRNA 5' end or possibly nt 27 and 26 In additionChemical modification of the siRNA seed region suppresses offtarget effects by steric hindrance to basepairing with targets Hanna Iribe,† Kengo Miyamoto,‡ Tomoko Takahashi,§ Yoshiaki Kobayashi,§ Jastina Leo,§ǁ Misako Aida,‡ and Kumiko UiTei†§* †Department of Computational Biology ad Medical Science, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo,Associated with the 59 region of the siRNA guide strand overlapping seed region 31, 32 These are analogous to the already known mechanism of RNA silencing Thus, a possible alternative pathway of RN is considered that siRNA seeddependent silencing on a transcriptional repressor causes the activation of downstream genes Recently, siRNA targeted to the HIV1 LTR promoter
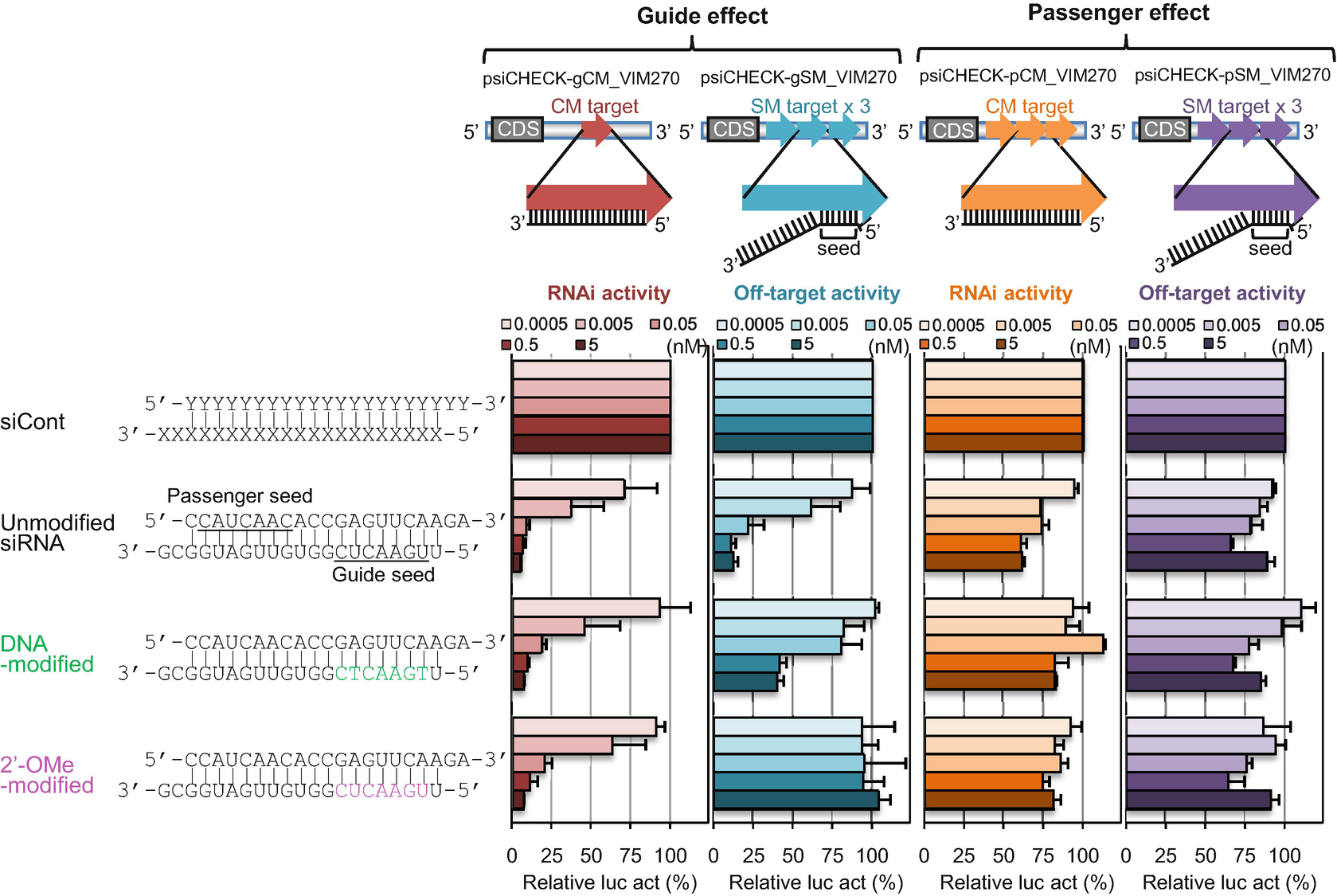
Between the siRNA seed region and target mRNA in an Aform helix11,12 The efficiency of the offtarget effect is positively correlated with the thermodynamic stability of the base pair between the guide strand seed region and SM transcripts10 Thus, siRNAs with low seed−target stability may be a promising tool for targetspecific RNAi with fewer offtarget effects However, theChemical modifications of 2'Omethyl (2'OMe) and locked nucleic acid (LNA) of the nucleotides in the seed region (positions 28) of the small interfering RNA (siRNA) guide strand significantly reduced seedmatched (SM) offtarget effects The siRNA with 2'OMe modifications inhibited the expression of a completelymatched (CM) target gene, whereas that with LNA modifications didThe siRNA Nonseed Region and Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants of OffTarget Effects Published in PLoS Computational Biology, December 15 DOI /journalpcbi Pubmed ID Authors Piotr J Kamola, Yuko Nakano, Tomoko Takahashi, Paul A Wilson, Kumiko UiTei Abstract RNA interference (RNAi) is a




Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects
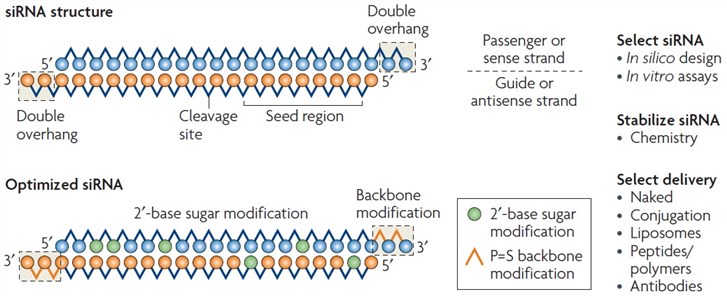
Blue circle, deoxyribonucleotide A) Both guideSmartBase TM siRNA Recommended Modifications 1 Alternating 2'F bases and 2'OMe bases in siRNA enhances duplex stability and are more resistant to RNase degradation 2 Use a few 2'OMe bases in the seed region of the guide strand to decrease the Tm below 215 of this region 2'O methyl base hybridization with RNA has a lower TM (5' end of It has been well established that siRNA offtarget effects are caused by the seed sequence of the siRNA (bases 2–8 of the guide strand) 7,10 Previous work demonstrated an enrichment of a specific seed region among the top screening hits 23 Furthermore, in Sudbery et al, 9 a statistical test was applied to identify 17 hexamer and 13 heptamer seed sequences




Pdf New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens Semantic Scholar




Ago Accessible Anticancer Sirnas Designed With Synergistic Mirna Like Activity Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
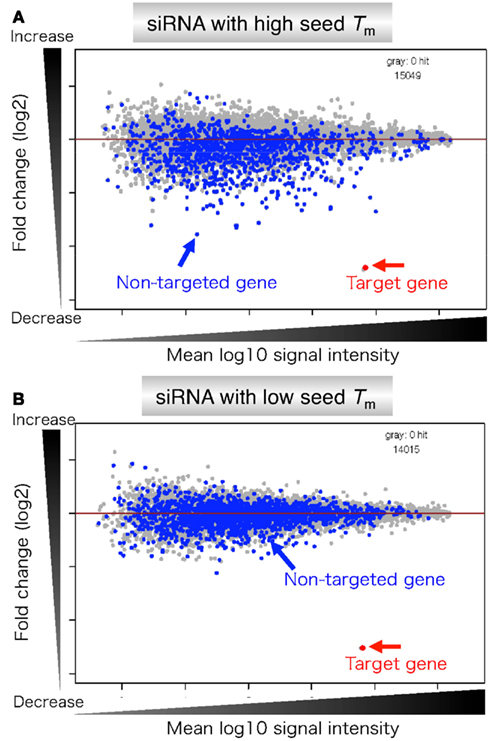
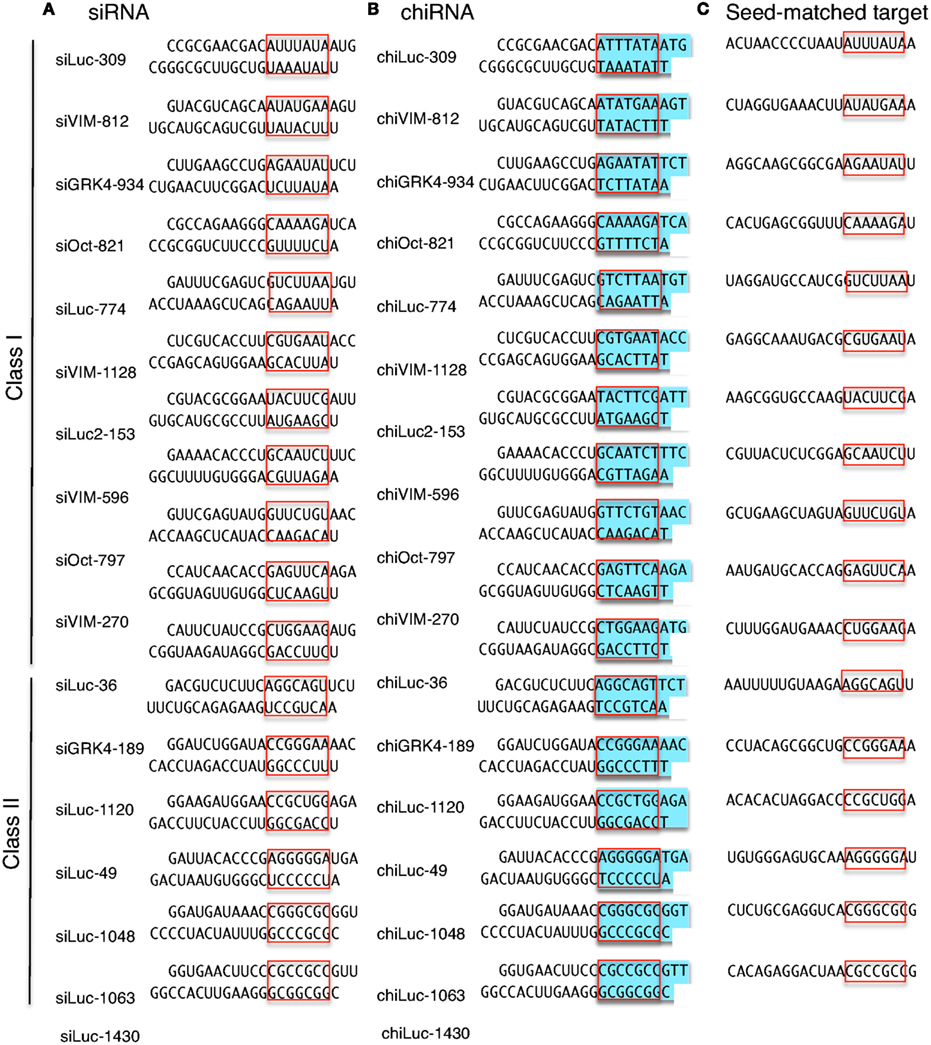
The results revealed that the seeddependent offtarget efficiency was positively and negatively correlated with the melting temperature (T m) (r = 074, Figure 2a) and standard free energy change (Δ G) (r = −069), respectively, calculated by the nearestneighbor procedure for the formation of the duplex between the siRNA seed region (positions 2–8) and the complementarySiDirect selects siRNAs with lower Tm value at the seed region, which contains 7 nucleotides at positions 28 from 5′ end of the guide strand siRNAs downregulate many unintended genes whose transcripts have complementarities to the siRNA seed region The capability of siRNA to induce this seeddependent offtarget effect is highly correlated with the thermodynamic stability of the Effects of 2bplong DNA substitutions in the nonseed region of siRNA (siLuc2153) with a dsDNA seed duplex on RNAi activity as determined by luc reporter assays Except for DNA/RNA difference, the nucleotide sequences of DNAmodified siRNAs used here were identical to that of siLuc2153 Red circle, ribonucleotide;




Selection Of Chemical Modifications In The Sirna Seed Region That Repress Off Target Effect Springerlink



Off Target Effects Dominate A Large Scale Rnai Screen For Modulators Of The Tgf B Pathway And Reveal Microrna Regulation Of Tgfbr2 Silence Full Text
Iribe H, Miyamoto K, Takahashi T, Kobayashi Y, Leo J, Aida M, UiTei K (17) Chemical modification of the siRNA seed region suppresses offtarget effects by steric hindrance to basepairing with targets ACS Omega 255–64 CrossRef Google Scholar 14 Xia T, SantaLucia J Jr, Burkard ME, Kierzek R, Schroeder SJ, Jiao X, Cox C, Turner DH (1998)Here, we demonstrate that both the melting temperature (Tm) in a subsection of siRNA nonseed region, and the GC contents of its corresponding target sequences, are negatively correlated with the efficiency of offtarget effect Analysis of experimentally validated miRNA targets demonstrated a similar trend, indicating a putative conserved mechanistic feature of seed regiondependentSize of seed region of siRNA we proposed is 68 bases Functional alignment Besides general sequence alignment, GenScript siRNA design tool incorporates a novel alignment approach, functional alignment This idea for functional aligment derives from asymmetry of siRNA in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex Antiviral motif filter Positive motif Positive motifs is a




2 O Methyl At Mer Guide Strand 3 Termini May Negatively Affect Target Silencing Activity Of Fully Chemically Modified Sirna Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia
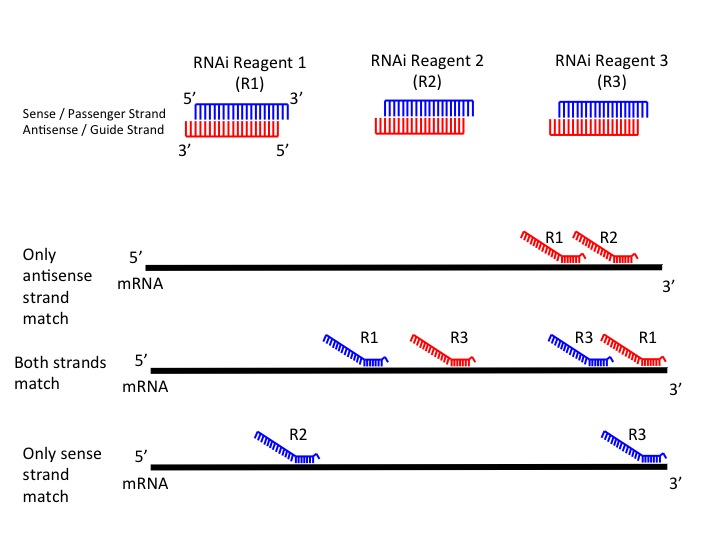
SiRNA screens is likely due to offtarget effects8 siRNA offtarget effects have been linked to the mechanism of action for miRNAs, 9 in which a short sequence on the 5′ end of the RNAi duplex (the "seed region," bases 2–8) is complementary to the 3′UTRs of multiple mRNAs, causing degradation of their associated transcripts7,10 BecauseEt al See more;Offtarget effects caused by the siRNA seed region Pooling of siRNAs better mimics the natural RNAi pathway and when combined with Thermo Scientific SMARTselection design, pooling provides advantages for both potency and specificity Advanced design filters to exclude siRNAs with conserved microRNA seedregion motifs Preference for lowerfrequency seed regions for



Ago Clip Based Imputation Of Potent Sirna Sequences Targeting Sars Cov 2 With Antifibrotic Mirna Like Activity Scientific Reports



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects Document Gale Academic Onefile
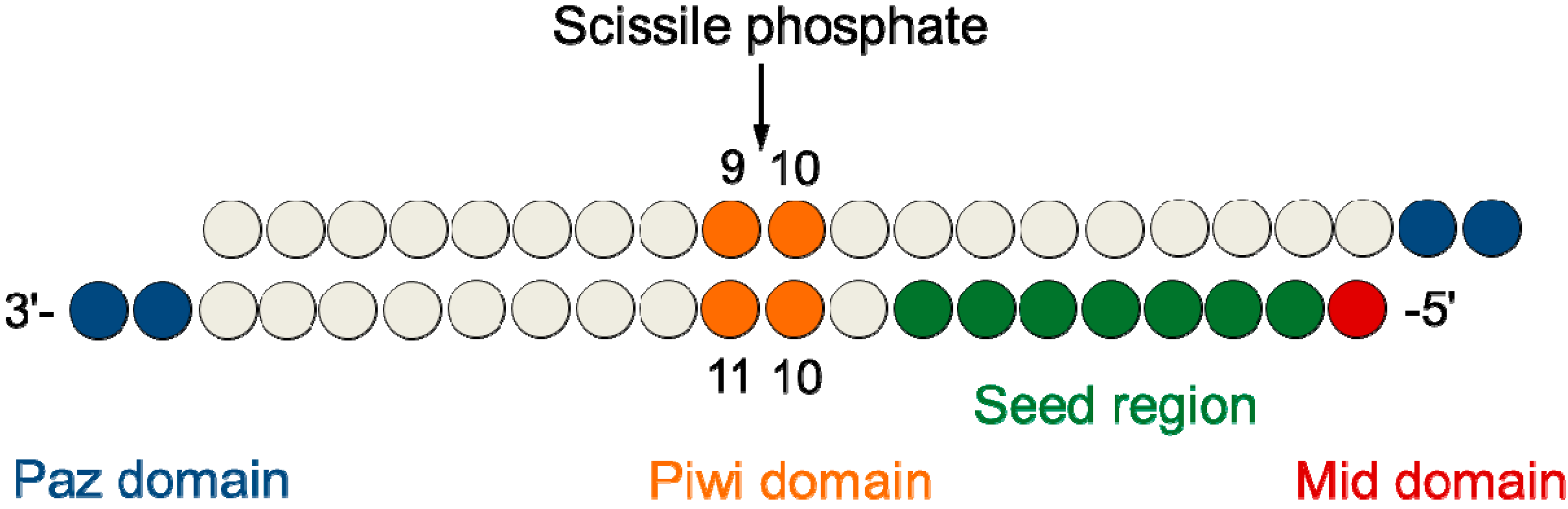
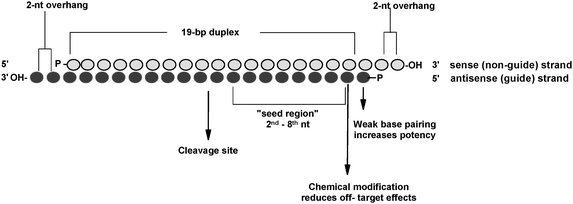
siRNA recognition of the target mRNA is conferred by the "seed region", a six nucleotide stretch corresponding to positions 27 on the antisense siRNA strand After the siRNA seed region anneals, the catalytic RNase H domain of Argonaute then subjects perfectly complementary mRNA sequences 10 nucleotides from the 5' end of the incorporated siRNAThe nonseed region of siRNA was found to be subdivided into four domains, in which two nucleotide pairs (positions 13 and 14) were replaceable with cognate deoxyribonucleotides without reducing RNAi activity However, RNA sequences at positions 912 and 1518 were essential for effective gene silencing, and these two doublestranded RNA cores are required for binding ofCompared with an siRNAlike approach, the requirement of perfect complementarity of the microRNA seed region to a given target sequence in the microRNA/target model has proven to be a more efficient strategy, accomplishing the selective targeting of pointmutated KRAS in vitro and in vivo artificial microRNA KRAS RNAi Single point mutations, categorized according to their




Nanomedicines Based On Recombinant Fusion Proteins For Targeting Therapeutic Sirna Oligonucleotides Therapeutic Delivery



Evaluation And Control Of Mirna Like Off Target Repression For Rna Interference Springerlink
By computational predictions of conformational changes of siRNA by these modifications, we revealed that both modifications in the siRNA seed region reduce SM offtarget effects by steric hindrance to basepairing with target transcripts but LNA modifications also disturb the association of the siRNA guide strand with the Argonaute (AGO) protein by altering Effects of 2bplong DNA substitutions in the nonseed region of siRNA (siLuc2153) with a dsDNA seed duplex on RNAi activity as determined by luc reporter assays Except for DNA/RNA differenceThe siRNA Nonseed Region and Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants of OffTarget Effects Kamola P;



1



Whole Genome Thermodynamic Analysis Reduces Sirna Off Target Effects
Seedregion analysis on siRNA designs reduces miRNAinduced offtargets A landmark publication (see Reference 2) from the Dharmacon research group was the first to experimentally demonstrate the key role of the seed region in mediating offtargets A subsequent 08 paper (see Reference 3) showed the importance of seed frequency in the 3' UTR as in indicator of itsA mutation in the seed region of miR96 causes hereditary progressive hearing loss A mutation in the seed region of miR184 causes hereditary keratoconus with anterior polar cataract Deletion of the miR17~92 cluster causes skeletal and growth defects Cancer Role of miRNA in a cancer cell The first human disease known to be associated with miRNA deregulation was chronicSeed region Thus, siRNA transcript silencing is sequence specific rather than target specific Examination of the signature transcripts downregulated with the same kinetics as the intended



Frontiers Sirna Finder Si Fi Software For Rnai Target Design And Off Target Prediction Plant Science



Exploring Paz 3 Overhang Interaction To Improve Sirna Specificity A Combined Experimental And Modeling Study Chemical Science Rsc Publishing
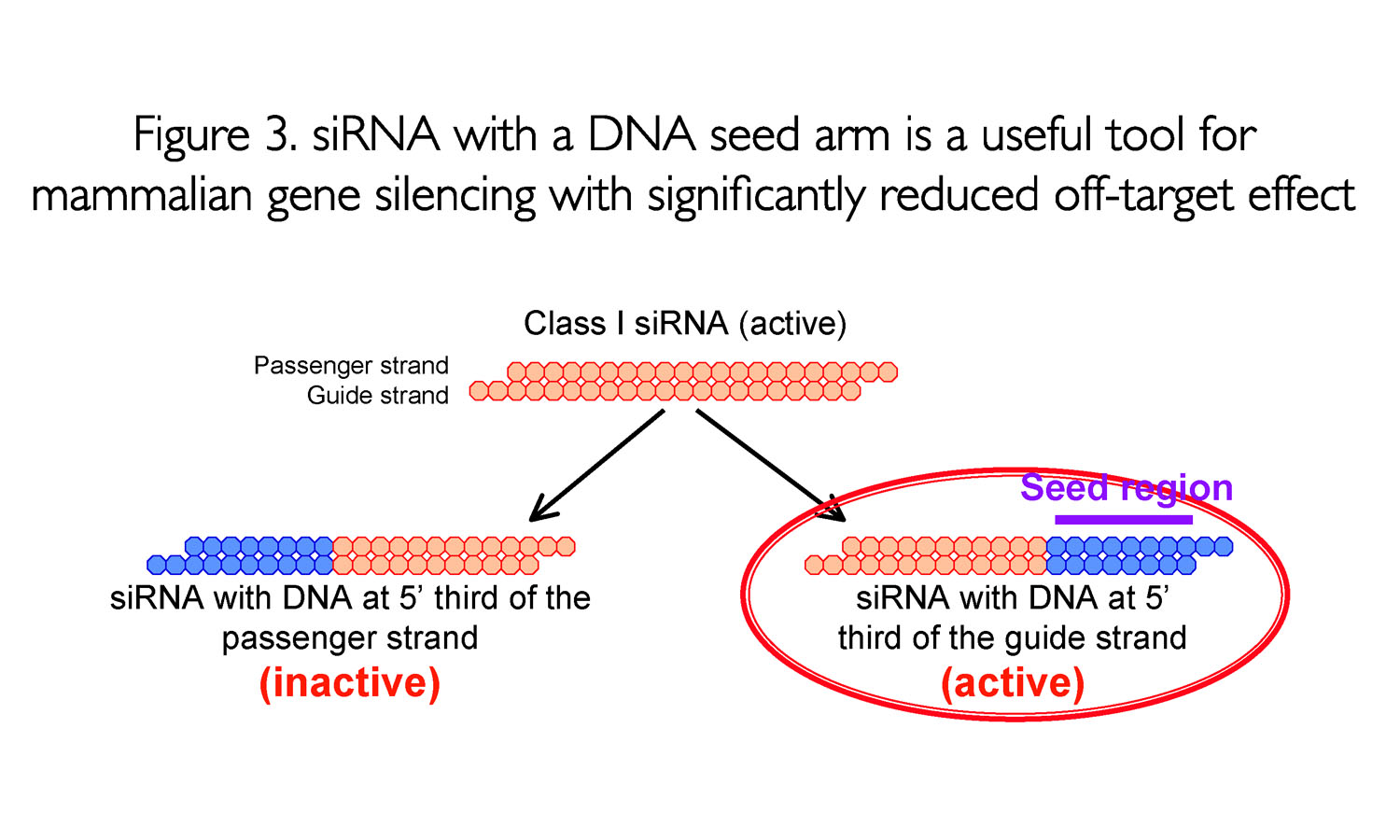
The nonseed region of siRNA was found to be subdivided into four domains, in which two nucleotide pairs (positions 13 and 14) were replaceable with cognate deoxyribonucleotides without reducing RNAi activity However, RNA sequences at positions 912 and 1518 were essential for effective gene silencing,So, we have looked for the rules that govern the capability of siRNAs to induce seeddependent offtarget effect, and revealed that the efficiency of offtarget effect is highly correlated to the thermodynamic stability of the duplex formed between the seed region of siRNA guide strand and its target mRNA (UiTei et al, 08) The stability between seed region and target mRNA is a determinant of the efficacy of siRNA offtarget effects 33 Thus, the high stability of the seed



Molecules Free Full Text Modulation Of The Rna Interference Activity Using Central Mismatched Sirnas And Acyclic Threoninol Nucleic Acids Atna Units Html




Structures Of Sirna A And Dna Seed Containing Sirna B The Download Scientific Diagram
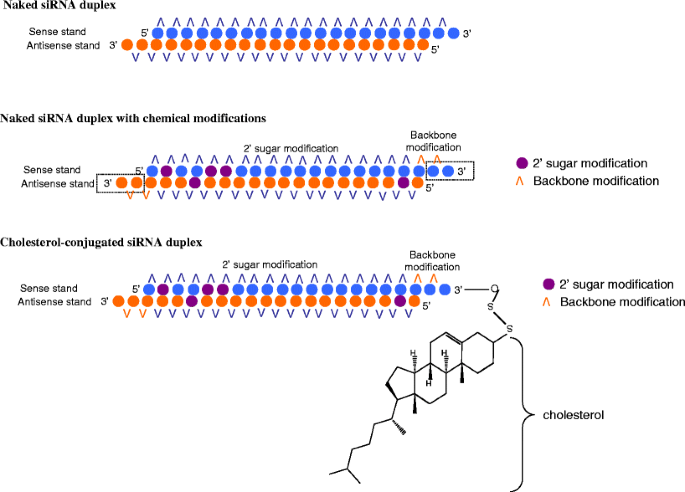
Asymmetric replacement of seed region nucleotides with DNA bases has also been shown to reduce offtargeting as a result of seed region complementarity within the passenger strand Recent in vitro studies have shown that shRNA produces fewer offtarget effects than siRNA Allows you to choose the region the siRNA targets (5' or 3' UTR or ORF), G/C percentage, and if you want to BLAST search the sequence Naito et al siDirect Identifies siRNA targets based on nucleotide sequence Provides location within the sequence, melting temperature of seed duplex, and a minimum number of mismatches against offtarget sequences Invitrogen• Alternating 2'F bases and 2'OMe bases in siRNA enhances duplex stability and are more resistant to RNase degradation • Use a few 2'OMe bases in the seed region of the guide strand to decrease the Tm below 215 of this region 2'O methyl base hybridization with RNA has a lower TM (5' end of guide or antisense strand has a seed




Ago Accessible Anticancer Sirnas Designed With Synergistic Mirna Like Activity Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids



Biological And Physicochemical Characterization Of Sirnas Modified With 2 2 Difluoro 2 Deoxycytidine Gemcitabine New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing
Every backbone phosphate of the seed nucleotides at positions 2–8 from the anchored 5′terminal nucleotide preordered on the AGO protein to make stable basepairing between the siRNA seed region and target mRNA in an Aform helix 11,12 The efficiency of the offtarget effect is positively correlated with the thermodynamic stability of the base pair between the guide strand seed regionPLoS Computational Biology (15) 11(12) DOI /journalpcbi 18 Citations Citations of this article 91 Readers Mendeley users who have this article in their library Add to library View PDF AbstractWhen the siRNA seed region (2–8 nts from the 50 end of the guide strand) base pairs with the unintended genes 6–10 (Fig 1) The offtarget effect is considered to be induced by the similar molecular mechanismwithmiRNAmediatedRNAsilencing,whichdiffers from the mechanism of RNAi Furthermore, the degree of offtarget effect is correlated positively with the thermodynamic



Specific Sirna Effect Left And Sirna Off Target Effects In Which Download Scientific Diagram



Selection Of Chemical Modifications In The Sirna Seed Region That Repress Off Target Effect Springerlink
Enhance siRNA effectiveness Seed region filters and seed frequency analysis for siRNA designs to minimize offtarget effects ONTARGETplus modifications reduce the overall number of offtargets, and pooling reduces them even further Offtargets induced by the indicated siRNA reagents targeting 5 genes were quantified by microarray analysis (Agilent 22K Platform) Panels A and BSeed region of the siRNA The immune response genes continued to be upregulated When the siRNA concentration was reduced to 1 nM, there was still a more than 2fold decrease in STAT3 mRNA levels, which was not significantly different than the levels observed at the higher siRNA doses (Figure 2A, S1, and Table 2) Importantly, STAT3 was the most significantly knockeddown




Pdf Functional Dissection Of Sirna Sequence By Systematic Dna Substitution Modified Sirna With A Dna Seed Arm Is A Powerful Tool For Mammalian Gene Silencing With Significantly Reduced Off Target Effect Semantic
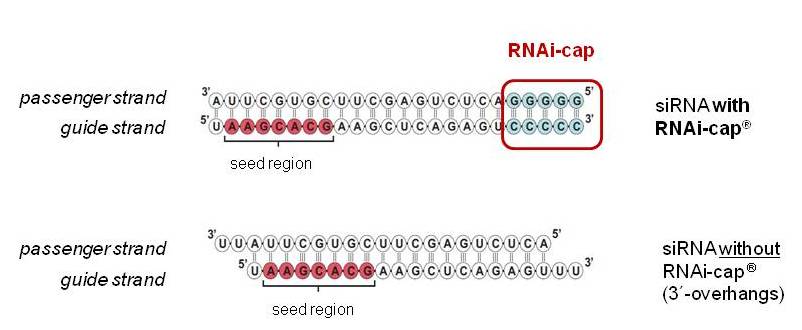



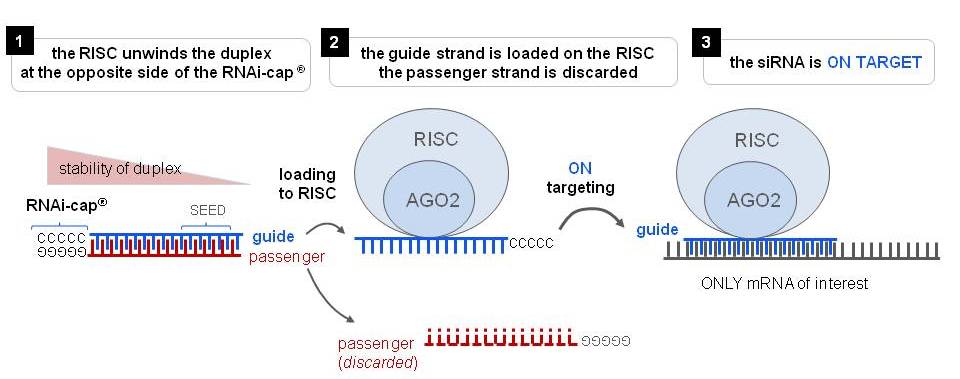
Riboxx Rna Technologies Better Silencing With Rnai Cap




Gene Silencing By 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Modified Sirna A Prodrug Type Sirna Responsive To Reducing Environment Sciencedirect



Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo




Pdf Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Semantic Scholar




An In Silico Analysis Of Effective Sirnas Against Covid 19 By Targeting The Leader Sequence Of Sars Cov 2 Pandey 21 Advances In Cell And Gene Therapy Wiley Online Library
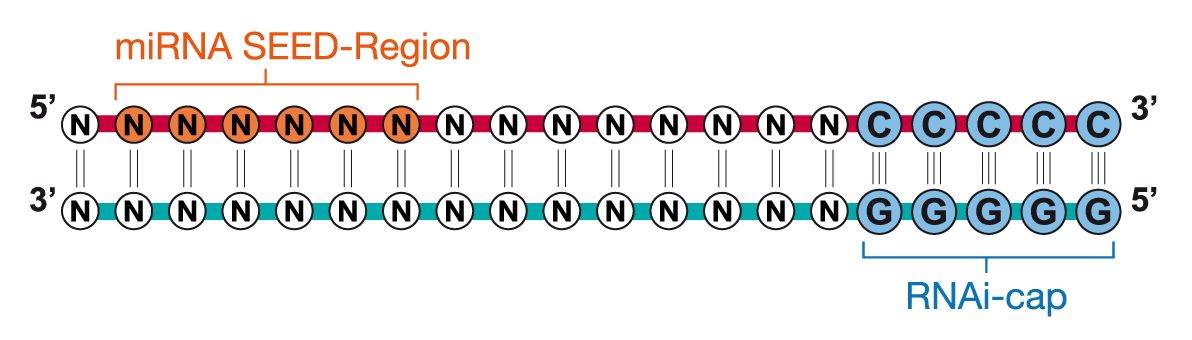



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna




Rational Design Of Highly Efficient Artificial Mirna Mirna Download Scientific Diagram




Graphical Representation Of Sirna Molecule A Sirna Duplex With Download Scientific Diagram




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link




Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife




Abundant Expression Of Maternal Sirnas Is A Conserved Feature Of Seed Development Pnas




Passenger Strand Cleavage Facilitates Assembly Of Sirna Into Ago2 Containing Rnai Enzyme Complexes Cell




Seed Dependant Off Target Effect The Capability Of Sirnas To Induce Download Scientific Diagram



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics



Gess



Unconventional Rna Interference Recent Approaches To Robust Rnai European Pharmaceutical Review



1




Seed Based Off Target Effects In Pooled Sirna Screens A An On Target Download Scientific Diagram




Sidesign Center User Guide




Ayn Cell Culture



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics



Plos One In Silico Design And Experimental Validation Of Sirnas Targeting Conserved Regions Of Multiple Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes
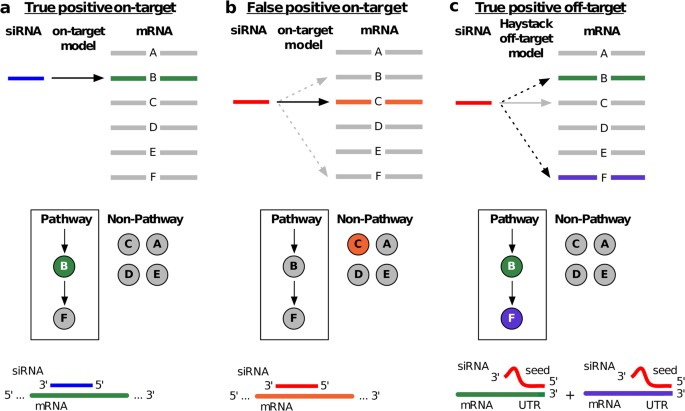



Sirna Off Target Effects In Genome Wide Screens Identify Signaling Pathway Members Scientific Reports
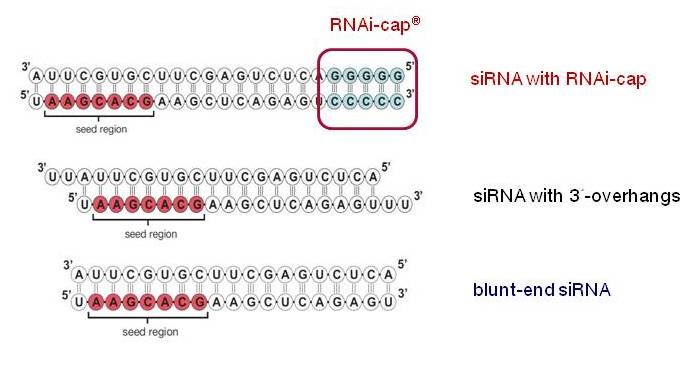



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna




Reduced Seed Region Based Off Target Activity With Lentivirus Mediated Rnai



2
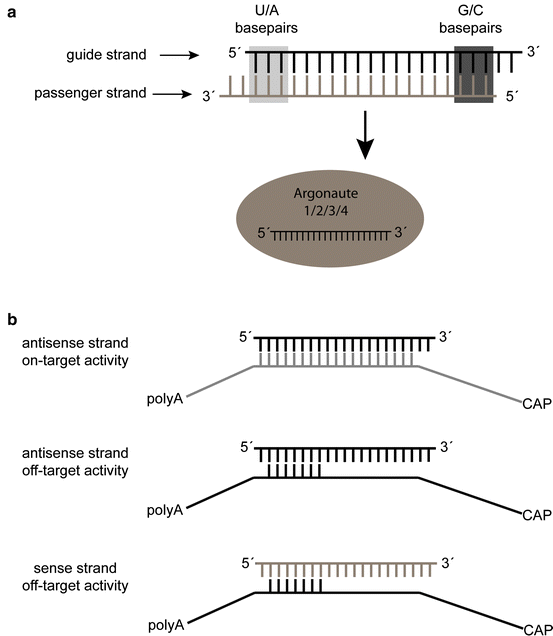



Sirna Design Principles And Off Target Effects Springerlink



2



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects
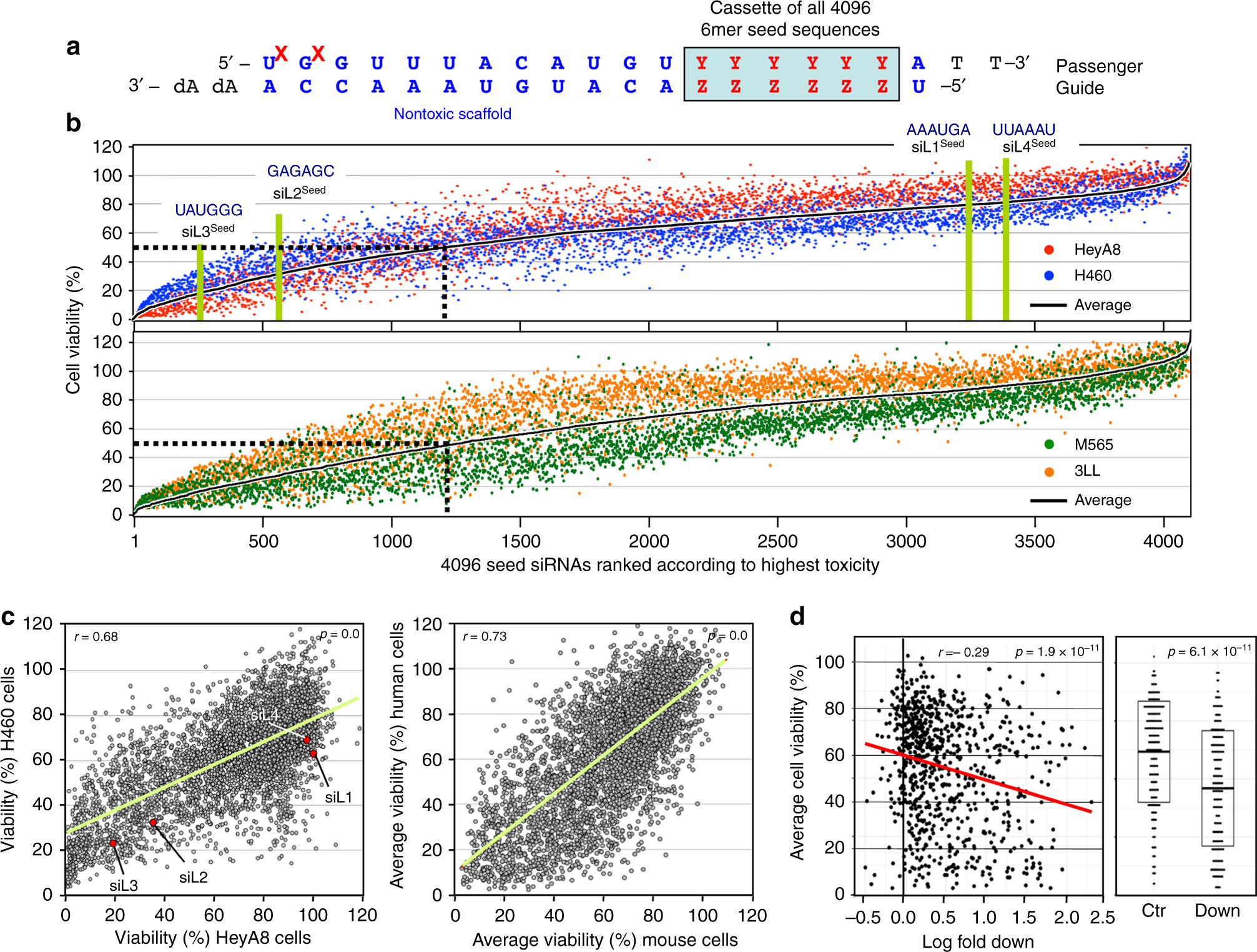



6mer Seed Toxicity In Tumor Suppressive Micrornas Nature Communications
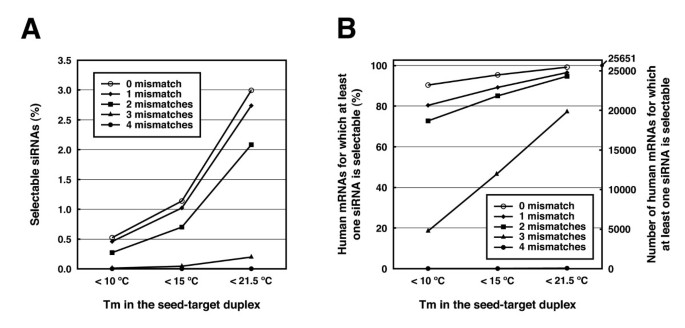



Sidirect 2 0 Updated Software For Designing Functional Sirna With Reduced Seed Dependent Off Target Effect Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text




Figure S1 Schematic Representation Of Amirna Vs Sirna Approach A Download Scientific Diagram




Pdf Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Semantic Scholar




Tolerance For Mismatches Between An Sirna And Its Target Sirna Seed Download Scientific Diagram




Sidirect 2 0 Updated Software For Designing Functional Sirna With Reduced Seed Dependent Off Target Effect Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text
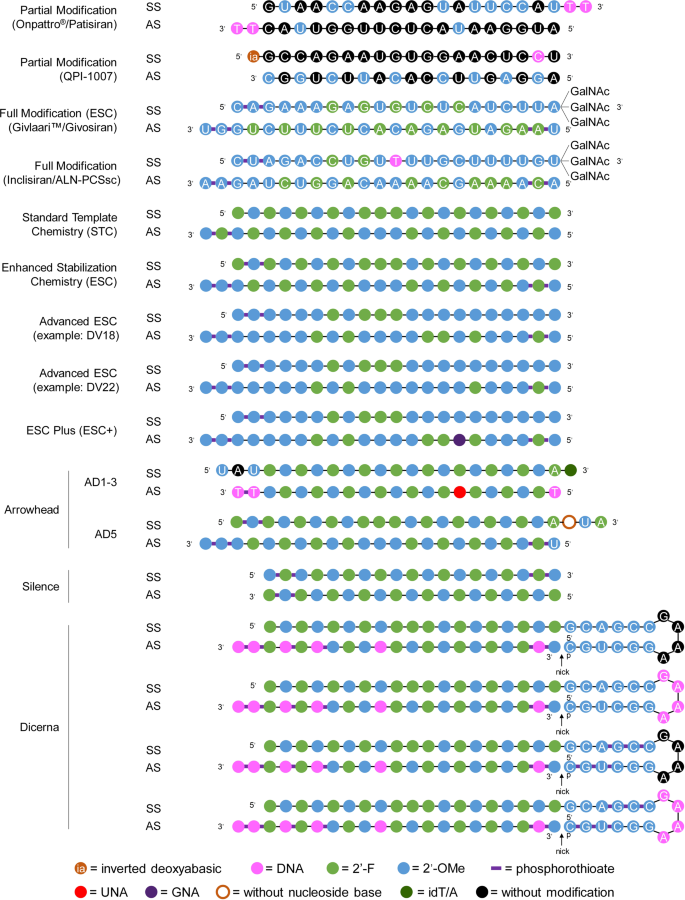



Therapeutic Sirna State Of The Art Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy




2 O Methyl At Mer Guide Strand 3 Termini May Negatively Affect Target Silencing Activity Of Fully Chemically Modified Sirna Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
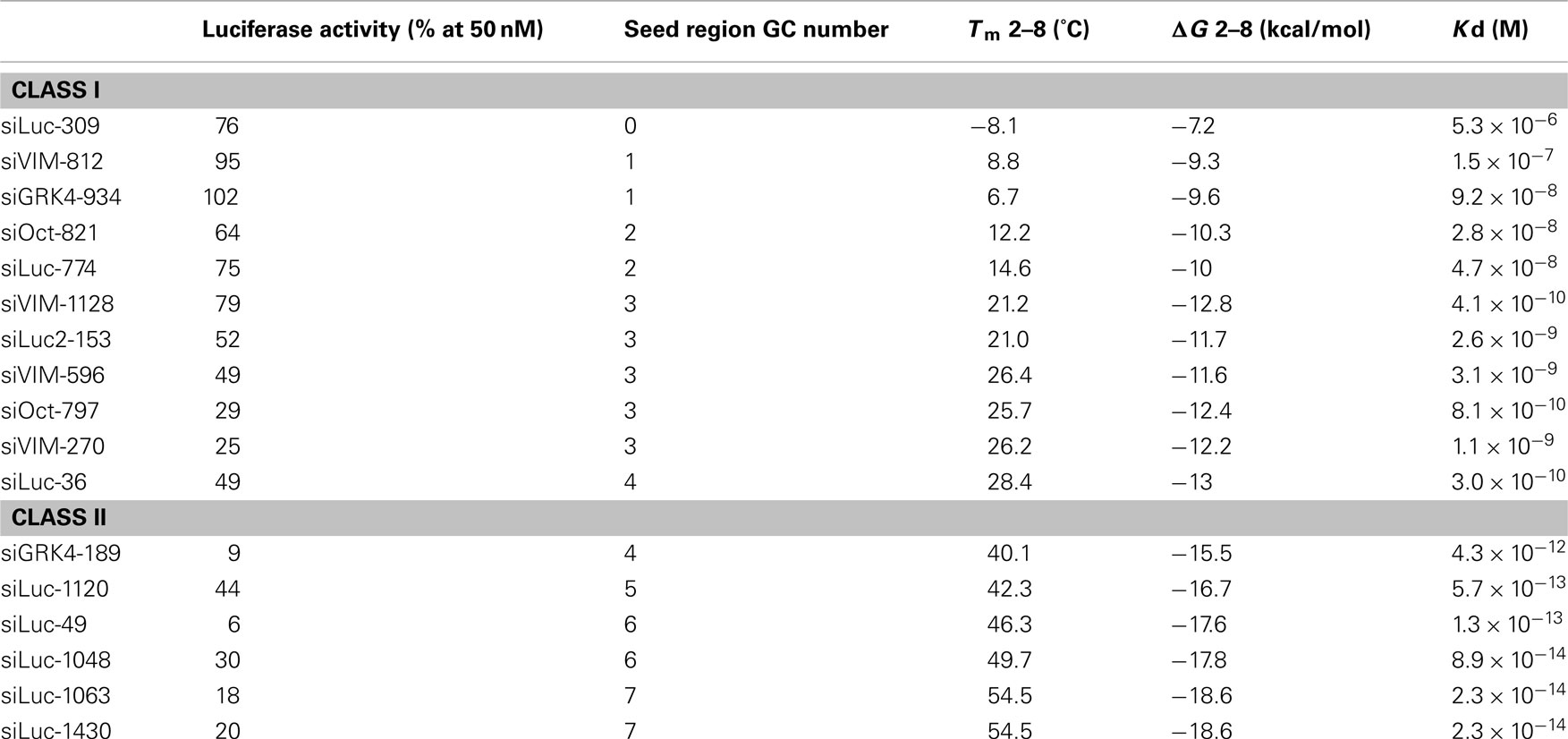



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics
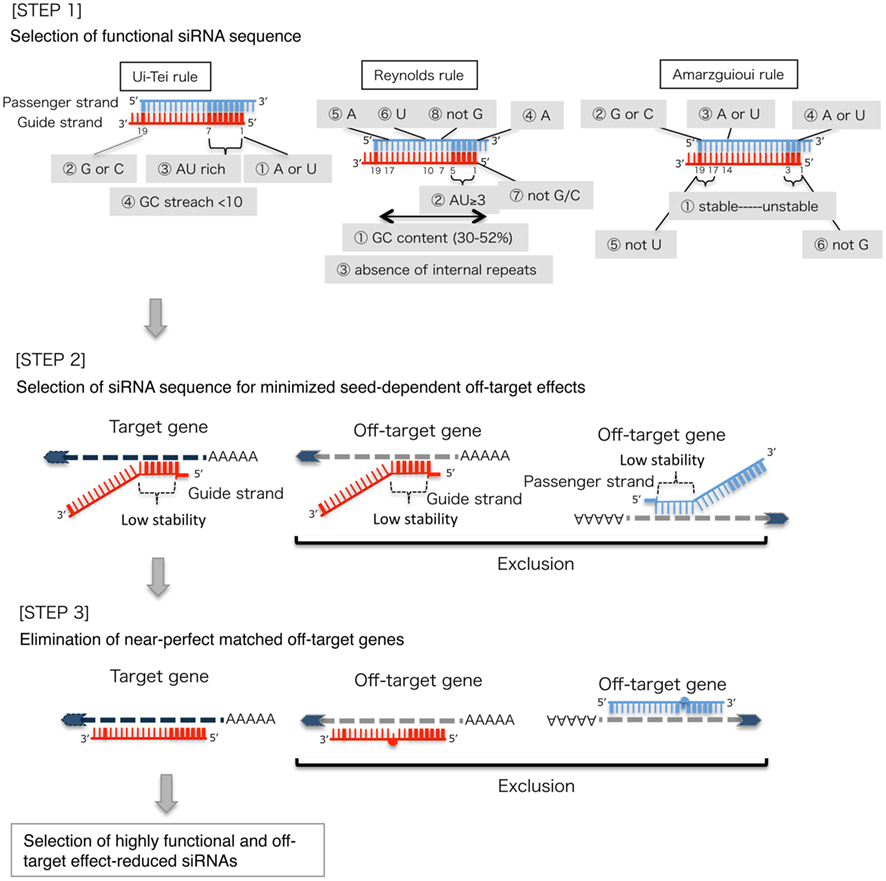



Frontiers Sirna Design Software For A Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Genetics



2




Effective Gene Silencing Activity Of Prodrug Type 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Sirna Compared With Non Prodrug Type 2 O Methyl Sirna Sciencedirect




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database




Structures Of Sirna A And Dna Seed Containing Sirna B The Download Scientific Diagram
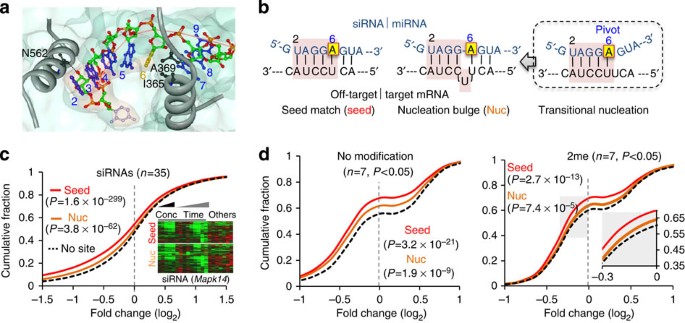



Abasic Pivot Substitution Harnesses Target Specificity Of Rna Interference Nature Communications
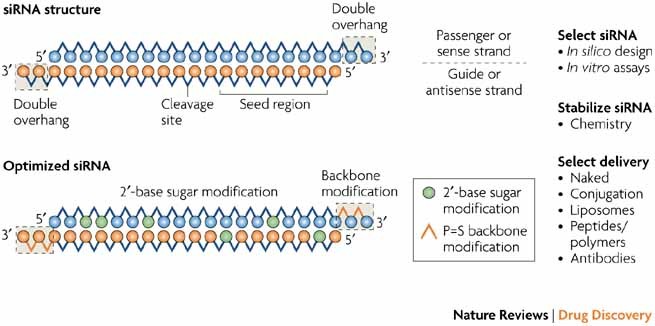



Interfering With Disease A Progress Report On Sirna Based Therapeutics Nature Reviews Drug Discovery
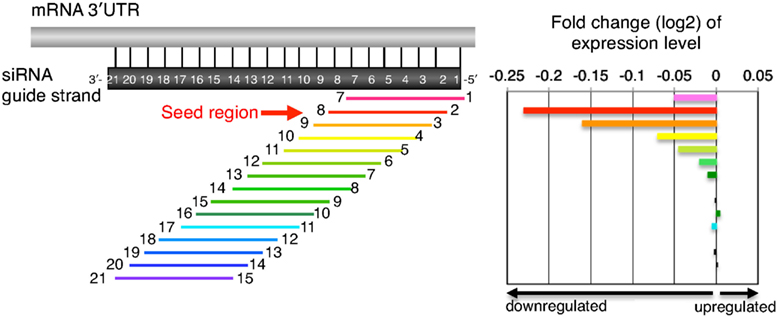



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics




Sirnas And Shrnas Tools For Protein Knockdown By Gene Silencing




Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo




Clinical Development Of Synthetic Sirna Therapeutics Sciencedirect



1
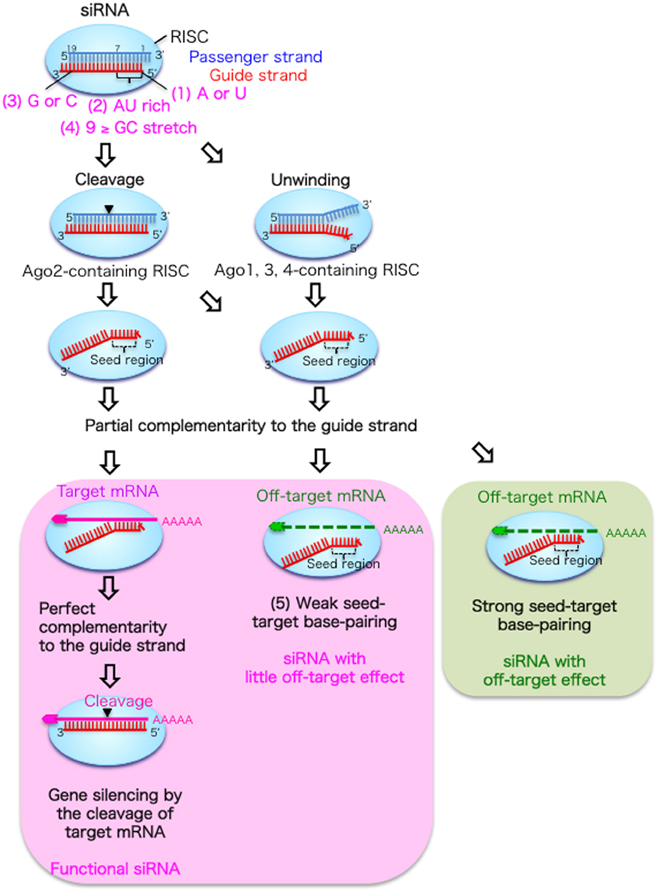



Frontiers Optimal Choice Of Functional And Off Target Effect Reduced Sirnas For Rnai Therapeutics Genetics



2




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Abstract Europe Pmc




Modified Sirna Structure With A Single Nucleotide Bulge Overcomes Conventional Sirna Mediated Off Target Silencing Molecular Therapy




A Simple And Cost Effective Approach For In Vitro Production Of Sliced Sirnas As Potent Triggers For Rnai Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids



1




A The Structure Of Sirna Sense And Antisense Strands And Target Mrna Download Scientific Diagram



Ijms Free Full Text Is The Efficiency Of Rna Silencing Evolutionarily Regulated Html



Frontiers Synthetic Rnas For Gene Regulation Design Principles And Computational Tools Bioengineering And Biotechnology



Rnai For Treating Hepatitis B Viral Infection Springerlink
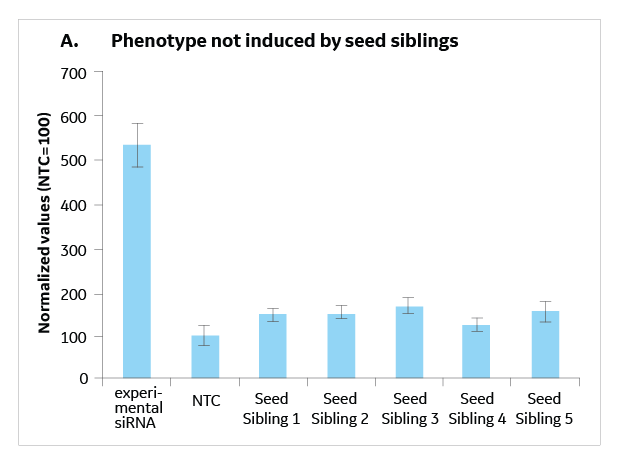



Seed Sibling Controls For Rnai Hit Validation



Sirna Shrna Oligo Optimal Design




Modification Of The Sirna Passenger Strand By 5 Nitroindole Dramatically Reduces Its Off Target Effects Zhang 12 Chembiochem Wiley Online Library




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal




Effects Of Dna Substitutions In The Non Seed Duplex Subdomains A B C Download Scientific Diagram



Sidirect




Sirna And Rnai Optimization Alagia 16 Wires Rna Wiley Online Library



Aln Vsp02 Creative Biolabs



New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens




Cell Free Reconstitution Reveals The Molecular Mechanisms For The Initiation Of Secondary Sirna Biogenesis In Plants Pnas



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Signature Transcript 39 Utrs Contain Sequence Complementarity To Sirna Download Scientific Diagram




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Sciencedirect
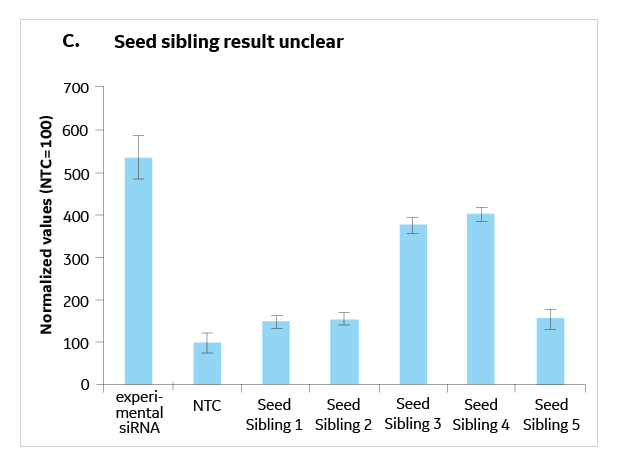



Seed Sibling Controls For Rnai Hit Validation




Figure 3 Specific Silencing Of L392v Psen1 Mutant Allele By Rna Interference



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database




Pdf The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects Semantic Scholar




Effects Of 2 Bp Long Dna Substitutions In The Non Seed Region Of Sirna Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿